0. License
Refer to Amateur Handbook from IMDA
Definitions
- ITC is International Telecommunication Convention
- ITU is International Telecommunication Union
- ERP is Effective radiated power
- PEP is Peak Emission Power
- Teleprinter / teletypewriter / Teletype / TTY is an electromechanical typewriter that can be used to send and receive typed messages from point to point and point to multipoint over various types of communications channels
- Telephony is the field of technology involving the development, application, and deployment of telecommunication services for the purpose of electronic transmission of voice, fax, or data, between distant parties.
- RTTY is Radio Teleprinter
- CHU is the call sign of a shortwave time signal radio station operated by the Institute for National Measurement Standards of the National Research Council of Canada
- WWVB is a time signal radio station near Fort Collins, Colorado and is operated by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
Exam format
- Section I Licensing Conditions
- 35 multiple-choice questions (1 hour)
- Syllabus:
- Licensing Conditions
- Operating Practices and Procedures
- Transmitter Interference
- Section II
- 60 multiple-choice questions (1 hour 45 minutes)
- Syllabus:
- Electrical Theory
- Semiconductors
- Radio Receivers and Transmitters
- Propagation and Aerials
- Measurement
Qualification required of the holder of Amateur Station License
- Amateur Station Licence for operating radio transmission/reception equipment.
- pass Radio Amateur’s Examination or qualification that is acceptable to IMDA
- IMDA may refuse without any reason
- Apply online via Telcom Licensing System
- Documents required: citizenship, results of the exam / valid cert, station license
- do not purchase equipment until it is approved
License fee
- license is renewable every 5 years
- license fee currently is $100
- license fee must be paid within 7 days of expiry of the license
- Late fees will be applicable afterwards.
- IMDA has waived the frequency application, processing fee and annual frequency usage fee
Important note:
- Admittedly, as of now, the exam is very old.
- Also, the current 2016 IMDA Handbook still reflects that the license is renewable annually and fee is $50
- Please check the IDA Handbook for any updates pertaining to changes in syllabus or regulations.
- Advised to follow latest IMDA Handbook in regards to this.
Amateur Station License
- be over
21 - above
16, the parents / guardian must sign off and be responsible for observation - radio amateur equipment is a model that is approved by IMDA
Operation of an Amateur Ratio Station
- Observer and comply with
- relevant provisions of the Telecommunications (Radio-communication) Regulations
- relevant provisions of the Radio Regulations of the ITC
- amateur station license shall be displayed, in close proximity of the equipment, at the station’s licensed address
- transmitting frequency bands allowed of an amateur radio station shall be at the discretion of IMDA
- frequency within the limits prescribed by the Radio Regulations, annexed to ITC of the ITU
Transmitting power
- power of the transmitter shall not exceed
300 watts (DC input) - does not cause radio frequency interference to other licensed or authorised stations or networks or telecommunication installation or equipment
- maximum RF output power allowed for the Restricted Class Station License is
10 watts (erp)
Operational conditions for the Station
- operated at locations approved by IMDA
- operated in the presence of the licensee
- licensee will be responsible for the proper operations of the station
- tuning of the transmitter must ensure a high degree of accuracy
- all emissions must be within the authorised bands
- no appreciable energy is radiated outside the frequency limits
- a satisfactory method of frequency stabilisation
- Equipment must be capable of verifying that the emissions are within the authorised bands
- station shall always be equipped with receiving as well as transmitting equipment
- all equipment must be erected, fixed, placed and used
- equipment should not interfere with the efficient and convenient working of other authorised stations
- must seek approval of any change of equipment, antenna installation, location and address
- the licensee must identify the transmission of a call sign assigned to him by IMDA at the beginning and end of each period of transmission
Transmission, Procedure & Limitation
- station may be operated at any time
- maximum of
10 minutesof continuous transmission - messages are
- allowed
- sent in plain language
- relate solely to the licensee’s experiments / personal affairs
- not allowed
- cannot relate to business affairs or transactions
- cannot be grossly offensive / indecent / obscene character
- allowed
- station cannot send:
- Government prohibited communication of this nature
- news
- advertisement
- communications of a business or non-experimental character
- messages for pecuniary / monetary reward
- messages for or on behalf of a third party
- Before making any call or test transmission, the frequency on which it is proposed to transmit should be monitored to ensure the transmission will not cause interference to other stations
- Calling other station
- call-sign of that stations shall be sent
3 ≤ times ≤ 8 - signal de for from shall be sent
once - call-sign of the calling station
3 times - call sent
3 timesat interval of2 minutes - calling shall cease and may not be resumed until after an interval
15 minutes
- call-sign of that stations shall be sent
- conversant with the accepted international Q codes
- call sign must be sent for identification purpose at the beginning and end of each period of transmission
- prefix for Singapore licensed stations is
9V
Telelphony
- use international accepted Phonetic Alphabet / figure guide
- words used in this manner will have a lesser chance of improper interpretation
Phonetic Alphabet
| Letter to transmit | Word to be used |
|---|---|
| A | Alfa |
| B | Bravo |
| C | Charlie |
| D | Delta |
| E | Echo |
| F | Foxtrot |
| G | Golf |
| H | Hotel |
| I | India |
| J | Juliet |
| K | Kilo |
| L | Lima |
| M | Mike |
| N | November |
| O | Oscar |
| P | Papa |
| Q | Quebec |
| R | Romeo |
| S | Sierra |
| T | Tango |
| U | Uniform |
| V | Victor |
| W | Whisky |
| X | X-ray |
| Y | Yankee |
| Z | Zulu |
Station log book
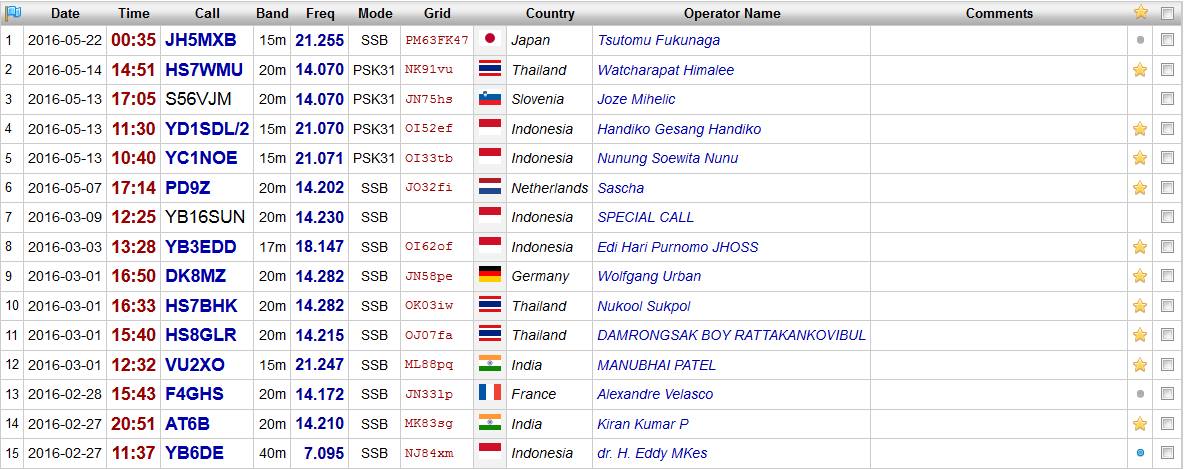
Image credit: 9V1AN’s public log
“Grid” column (optional): Maidenhead system for location
- indelible (of ink or a pen making marks that cannot be removed) record shall be kept in a log-book
- serially numbered
- date and time of commencement and ending of every call made from the station
- call-signs of the stations from which messages addressed to
- time (local or GMT) of the commencement and termination
- test transmissions of the station
- frequency band(s) and class or classes of emission in each case
- frequency in
MHz - mode
SSB, PSK, etc - band in
m
- frequency in
- no gaps shall be left between entries
- all entries shall be made at the time of sending and receiving
- the record shall be signed at the time of recording by the licensee
- log book shall be kept for at least 2 years
- be available for examination at all reasonable times by an authorised officer of IMDA
Interference
- Equipment must be designed, constructed, maintained and used in the operation of the station to avoid interference
- Operator must not cause any harmful interference to other authorised radio services or stations
- In the case of interference, the licensee shall take all possible steps to eliminate the source of such interference
- Precautions:
- avoid over-modulation
- keep the radiated energy within the narrowest possible frequency bands
- radiation of harmonics and spurious emissions shall be suppressed
- tests shall be made from time to time and details of those tests shall be recorded in the station log-book
- Adjustment of an amateur station shall, in general, be made by using a dummy load
Portable / Mobile station
- only operate in the frequency bands
- only be allowed to operate in Singapore
- mobile / portable station and the general station cannot be operated simultaneously
- the call-sign = general station followed by
/Mor/P - transmitter output power of the portable station shall not exceed
10 watts (erp) - licence may be modified or revoked at any time by IMDA without assigning any reason therefor
- it is readily movable from place to place to be operated therefrom
- station fee of $50.00 per mobile/portable station is waived
- station shall be closed down at any time on the demand of an authorised officer acting under the authority of IMDA
Frequency checking equipment in amateur stations
- A licensee must:
- be able to verify that his transmissions are within the authorised frequency band
- no appreciable energy is radiated outside the band
- use a satisfactory method of frequency control
- transmissions do not contain unwanted frequencies
- transmission do not contain harmonics and spurious frequencies
- station requires a crystal reference source
- with a transmitter (crystal-controlled)
- an absorption device of suitable frequency range and accuracy is necessary
- check that the desired harmonic of the crystal frequency is selected
- with a transmitter (not crystal-controlled) - a wavemeter based on a crystal oscillator is necessary
- with a transmitter (crystal-controlled)
- Frequency measuring equipment
- should be of sufficient accuracy
- an accuracy of
±1.0%: operation in the centre of the21.0 MHz - 21.45 MHzband - an accuracy of
±0.05%:10 kHzof band-edge
- an accuracy of
- verify that emissions are within the authorised frequency bands
- should be of sufficient accuracy
- Heterodyne wavemeters and crystal calibrators
- frequencies up to
4 MHz:100 kHzcrystal is usually adequate - higher frequencies:
500 kHzcrystal or preferably1 MHz
- frequencies up to
- Absorption wavemeters and similar devices
- scale length and accuracy should be suitable for measurements of the required accuracy to be made
- the frequency coverage must extend up to the second and preferably the third harmonic of the radiated frequency
- For VHF and UHF transmitters
- best technique is to measure the frequency of the fundamental oscillator as accurately as possible
- use an absorption device to confirm that the wanted harmonic has been selected
- VHF or UHF converter
- the calibration of the main receiver can be checked with sufficient accuracy
- also advisable to use an absorption wavemeter to check the measurement and to confirm that no unwanted radiations are present
Frequency bands, power and classes of emissions
| Conditions | Frequency Bands (in MHz) |
Classes of Emission | Maximum DC Input Power | RF Output PEP for A1, A2 and A3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - shared by other services - RTTY may not be used |
1.8 - 2.0 |
A1A, A1B, A2A, A2B F1A, F1B, F2A, F2B A3E, R3E, G3E, H3E, J3E, F3E |
10 watts | 26.67 watts |
| - shared by other services | 3.5 - 3.9 |
same as above | 300 watts | 800 watts |
band 10.1 - 10.15 is allocated on secondary basis |
7 - 7.10, 10.1 - 10.15, 14 - 14.35, 18.068 - 18.168, 21 - 21.45, 24.890 - 24.990, 28 - 29.7 |
same as above | 300 watts | 800 watts |
| - need consent from IDA - CW operators use the lower band - other classes of emission use the mid and upper band |
144 – 146 |
same as above | - | 25 watts |
| - need consent from IDA (include power, conditions, operations) - shared by other services - only certain spot Frequencies are allocated in Amateur Service - |
430 – 440 |
same as above | - | Table below |
| same as above | 1240 - 1300, 2300 - 2450, 3300 - 3500, 5650 - 5850, 10000 - 10500 |
same as above | Subject to licensing conditions | |
| same as above | 24,000 - 24,050 24,050 - 24,250 |
same as above | Subject to licensing conditions | |
| same as above | 2,350 - 2,400, 5,700 - 5,800 |
K1A, K2A, L2A, K2E and L3E | - | As above |
Band plan and spot frequency
| # | Band (MHz) | Mode | Frequencies (MHz) | Maximum Output Power |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 432.000 - 432.150 | Continuous Wave (CW) only | 432.000 | 10 watts erp |
| 2 | 432.150 - 432.500 | Single-Sideband (SSB) and CW only | 432.200 | 10 watts erp |
| 3 | 432.500 - 432.800 | Radio Teleprinter (RTTY) Facsimile (FAX) | 432.600 | 10 watts erp |
| 4 | 433.375 - 434.600 | FM Simplex Channels | 433.625, 433.650 | 10 watts erp |
Modulation symbols
The ITU uses an internationally agreed system for classifying radio frequency signals. Each type of radio emission is classified according to its bandwidth, method of modulation, nature of the modulating signal, and type of information transmitted on the carrier signal. It is based on characteristics of the signal, not on the transmitter used.
Modulation types (1st digit)
| Symbol | Modulation | Carrier | Sideband | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | amplitude | Double | AM broadcast radio | |
| R | reduced or variable | Single | ||
| G | phase | |||
| H | full | Single | as used by CHU | |
| F | frequency | FM broadcast radio | ||
| J | suppressed | Single | Shortwave utility and amateur stations | |
| K | pulse amplitude | |||
| L | pulse width | used by WWVB |
Type of modulating signal (2nd digit)
| Number | Channel | Info | Subcarrier | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | No modulating signal | |||
| 1 | One | digital | none | without modulating audio frequency |
| 2 | One | digital | using | with modulating audio frequency |
| 3 | One | analog |
Type of transmitted information (3rd digit)
| Symbol | Type | Decoded by | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | No transmitted information | ||
| A | Aural Telegraphy | by ear | Morse code |
| B | Electronic Telegraphy (Teletype) | radioteletype and digital modes | |
| E | Telephony | by human | voice or music |
More Examples:
| No. | Type | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Amplitude Modulation | A1A | Morse telegraphy |
| 2 | Amplitude Modulation | A1B | Teletype telegraphy |
| 3 | Amplitude Modulation | A2A | Morse telegraphy |
| 4 | Amplitude Modulation | A2B | Teletype telegraphy |
| 5 | Amplitude Modulation | A3E | Telephony, double-sideband |
| 6 | Amplitude Modulation | R3E | Telephony, single-sideband, reduced carrier |
| 7 | Amplitude Modulation | H3E | Telephony, single-sideband, full carrier |
| 8 | Amplitude Modulation | J3E | Telephony, single-sideband, suppressed carrier |
| 1 | Frequency Modulation | F1A | Morse telegraphy by frequency-shift keying |
| 2 | Frequency Modulation | F1B | Teletype telegraphy by frequency-shift keying |
| 3 | Frequency Modulation | F2A | Morse telegraphy by on-off keying of frequency-modulating audio frequency |
| 4 | Frequency Modulation | F2B | Teletype telegraphy by on-off keying of frequency-modulating audio frequency |
| 5 | Frequency Modulation | F3E | Telephony by frequency modulation |
| 6 | Frequency Modulation | G3E | Telephony by phase modulation |
| 1 | Pulse Modulation | K1A | Telegraphy by on-off keying of a pulse carrier |
| 2 | Pulse Modulation | K2A | - Telegraphy by on-off keying of a modulating audio frequency or frequencies or by on-off keying of a modulated pulse carrier - the audio frequency or frequencies modulating the amplitude of the pulses. |
| 3 | Pulse Modulation | L2A | - Telegraphy by on-off keying of a modulating audio frequency or frequencies or by on- off keying of a modulated pulsed carrier - the audio frequency of frequencies modulating the width (or duration) of the pulses. |
| 4 | Pulse Modulation | K2E | Telephony, amplitude modulated pulses |
| 5 | Pulse Modulation | L3E | Telephony, width (or duration) modulated pulses |
International Q Codes
| Type | Question | Answer | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | QRG | frequency | Will you tell me my exact frequency? | Your exact frequency is __ kHz |
| 2 | QRH | frequency | Does my frequency vary? | Your frequency varies |
| 3 | QRI | frequency | What is the tone of my transmission? | The tone of your transmission is (a) good, (b) variable, (c) bad |
| x | QRJ | x | x | |
| 5 | QRK | interference | What is the intelligibility of my signals? | The intelligibility of your signals is (a) bad, (b) poor, (c) fair, (d) good, (e) excellent |
| 6 | QRL | interference | Are you busy? | I am busy. Please do not interfere. |
| 7 | QRM | interference | Is my transmission being interfered with? | Your transmission is being interfered with (a) nil, (b) slightly, (c) moderately, (d) severely, (e) extremely |
| 8 | QRN | interference | Are you troubled by static? | I am troubled by static (a) nil, (b) slightly, (c) moderately, (d) severely, (e) extremely |
| 9 | QRO | power | Shall I increase transmitter power? | Increase transmitter power |
| 10 | QRP | power | Shall I decrease transmitter power? | Decrease transmitter power |
| 11 | QRQ | speed | Shall I send faster? | Send faster ( ___ words per minute) |
| 12 | QRS | speed | Shall I send slowly? | Send more slowly ( ___ words per minute) |
| 13 | QRT | speed | Shall I stop sending? | Stop sending |
| 14 | QRU | call | Are you ready? | I am ready |
| 16 | QRX | call | When will you call me again? | I will call you again at __ hours on __ kHz |
| 17 | QRZ | call | Who is calling me? | You are being called by __ on __ kHz |
| 18 | QSA | signals | What is the strength of my signals? | The strength of your signals is (a) scarcely perceptible, (b) weak, (c) fairly good, (d) good, (e) very good |
| 19 | QSB | signals | Are my signals fading? | Your signals are fading |
| 20 | QSD | signals | Are my signals mutilated? | Your signals are mutilated |
| 21 | QSL | communicate | Can you acknowledge receipt? | I am acknowledging receipt |
| 22 | QSO | communicate | Can you communicate with ___ direct? | I can communication with ___ direct |
| 23 | QSP | communicate | Will you relay to ___ | I will relay to ___ |
| 24 | QSV | communicate | Shall I send a series of V’s for adjustment on this frequency? | Send a series of V’s. |
| 25 | QSZ | communicate | Shall I send each word or group more than once? | Send each word or group twice |
| 26 | QTH | location | What is your location? | My location is ___ |
| 27 | QTR | time | What is the correct time? | The correct time is ___ hours. |